ISI is part of a consortium that has won funding to develop in-situ process analytical technologies (PAT) for freeze-drying, a key element in the manufacturing and distribution of vaccines and biological drug therapies. Widely adopted, the novel PAT will deliver substantial cost savings and environmental benefits, while shortening development times. It will also help align the pharma-manufacturing sector with the UK Clean Growth Strategy. This project, named Digital_Lyo, is part of the UK government’s Digitalisation and Automation of Medicines R&D and manufacture competition funded through Innovate UK.
Background
The number of biopharmaceutical injectable products is increasing. Currently, for 40% of biopharmaceuticals (EurPharmRev2018), including those repurposed for COVID-19, freeze-drying (lyophilisation) is the only method enabling an acceptable shelf life without refrigeration or cold-chain infrastructure. However, freeze-drying is a wasteful, energy-intensive, batch process with long processing times. Therefore, cold chain distribution is essential to maintain product viability. Hence, the manufacture and distribution of products contribute significantly to global carbon emissions.
Freeze-drying removes water from sensitive or high-value products such as vaccines. It takes between 24 and 96 hours, and the product’s quality can only be assessed at the end of the cycle. This results in increased energy consumption, CO2 emissions, loss of valuable product, and increased environmental bioburden. Furthermore, freeze-drying uses environmentally dangerous refrigerants (classified as having a high global warming potential, or GWP, and banned from 2030) or liquid nitrogen (high energy use in manufacturing) for cooling.
The Digital_Lyo Project
Through the Digital _Lyo project, the consortium is developing a unique, first-of-its-kind multi-PAT freeze-dryer suitable for laboratory-scale freeze-dryers. Potentially, it will be possible to retrofit to existing systems.
Aims:
- Reduce freeze-drying cycle time, leading to increased use of freeze-drying equipment, typically located in high-energy-consuming good manufacturing process (GMP) facilities.
- Reduce losses and batch failures to reduce wastage/bioburden.
- Shorten development times through increased reliability of data in clinical trials,
- Increase process robustness to improve product quality and consistency.
- Significantly enhance drying economies by facilitating the development and adoption of new, continuous processes.
- Enable more sustainable pharmaceutical product supply chains, which are key to the treatment and prevention of multiple diseases.
- Align the pharma-manufacturing sector with the UK Clean Growth Strategy.
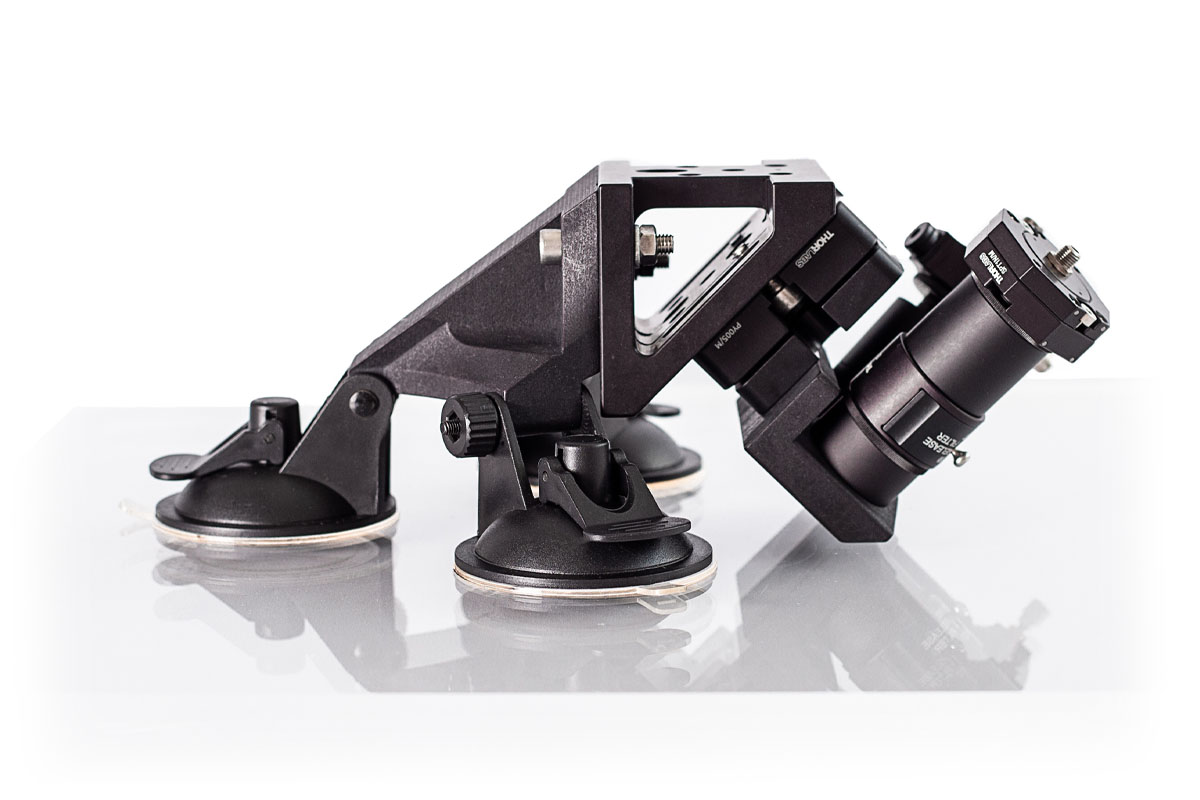
Digital_Lyo will use real-time, multiplexed Process Analytical Technology (multi-PAT-lyo) to integrate and exploit process signatures from inline impedance spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and accurate vapour-sensing technology. These will be used to generate large, information-rich data sets, suitable for modelling and process feedback.
The Project Team
Lyosenz (Lead, formerly Micron Design) provides a complete engineering service from design concepts through manufactured prototypes to production. They are developing a precision broadband impedance spectrometer for fast measurements of the freeze-drying process and will oversee the whole project.
IS-Instruments is responsible for determining the optimum Raman excitation wavelength, developing the Digital_Lyo Raman System, and overseeing the system integration.
Siemens Process Systems Engineering Ltd – Digital Process Twin technology supplier to the process industries. SPSE is providing and enhancing its digital-twin models to enable novel PAT methods and the development of robust lyophilisation processes.
DMU is responsible for developing the analytical routines to map impedance data to freeze-drying process parameters.
AstraZeneca Plc – a global, science-led biopharmaceutical company with extensive expertise in freeze-drying complex pharmaceutical formulations. The company provides strategic leadership to guide the project’s industrial direction and ensures access to relevant facilities and assets. Experienced scientists support the consortium by evaluating new PAT tools and generating high-quality data for model development and validation.
Qrometric Ltd – UK metrology company specialising in measuring and calibrating temperature and humidity. They are optimising the required humidity/vapour pressure metrology to develop the Digital_Lyo model for secondary drying.
Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency – regulates medicines, medical devices and blood components for transfusion in the UK. They are assisting with lyophilisation development through experience in formulation/standards development, and the validation of Digital_Lyo approaches to formulation and process design.
Measuring Success
The successful development of multi-PAT-Lyo will provide the biopharmaceutical sector with robust, scalable methodologies for process monitoring and control. This capability will support advanced therapeutics, including fusion proteins, gene therapies, and monoclonal antibodies. Improved process understanding will enable faster, more reliable manufacturing and accelerate patient access to novel, life-changing treatments.
Our end-user evaluators, who will derive direct and immediate benefits from the application of Digital_lyo technologies, are AstraZeneca (manufacturer of innovator products and new modalities) and the Biological Standards Laboratory at the MHRA, South Mimms.
This project builds on our work with DMU on the AtlasBio project (Ref 102610) – through-vial impedance spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy for data synergy across multiple scale lengths.